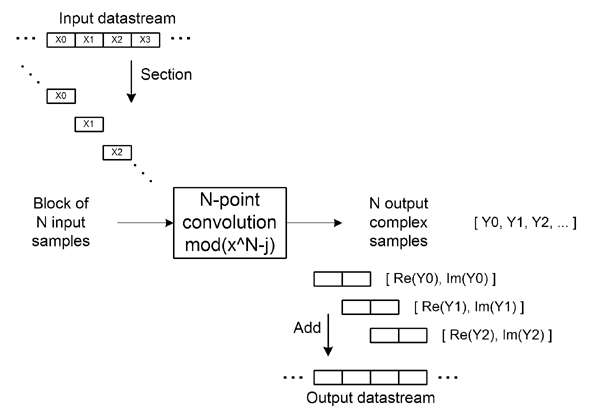
Block convoluiton using skew transform (overlap-add method)
Contents
Overlap-add method
function []=overlapaddqdft_demo()
% Classic overlap-add method is using FFT size of 2N, where N is block size [1]. % Proposed method is using skew transform of size N for computation reduction [2]. % Convolution mod(x^N-j) is used for each block, and the skew transform is % an eigen transform of this skew convolution. % It is easy to see that multiplication of two polynomials y(z)=x(z)*h(z) (mod (x^N-j)), % where x(z)=x(0)+x(1)*z+x(2)*z^2+..+x(N-1)*z^(N-1) is an input signal, % and h(z)=h(0)+h(1)*z+h(2)*z^2+..+h(N-1)*z^(N-1) is impulse response of a filter, % will give result of block convolution % if output is read as Y=[Re(y(0))... Re(y(N-1)), Im(y(0))... Im(y(N-1))].
Init
N=32; % block size x=randn(1,5*N); % input signal h=randn(1,N); % filter impulse response % y=fftfilt(h,x); % true result
Classic overlap-add method (FFT size = 2*N)

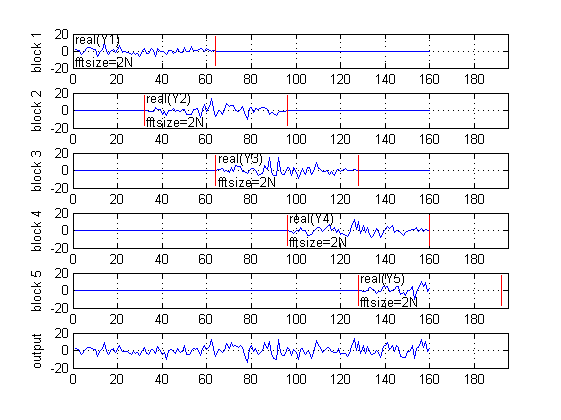
hs=fft(h',2*N); % filter spectral response xn=reshape(x,N,[]); xn=[xn; zeros(size(xn))]; xs=fft(xn); % block spectrum of input signal (FFT size = 2*N) ys=bsxfun(@times,hs,xs); % spectral domain multiplication y1=real(ifft(ys)); % block convolution result y2=y1(1:N,:)+[zeros(N,1) y1((1:N)+N,1:end-1)]; % overlap-add block combination ycl=reshape(y2,[],1); % block-wise graph figure(2) plot_blockwise_classic(y1,N,length(x)) subplot(size(y1,2)+1,1,size(y1,2)+1); plot(ycl) axis([0 round(length(x)+N*1.1) -20 20]); grid on ylabel(['output']);
Proposed overlap-add method (FFT size = N)
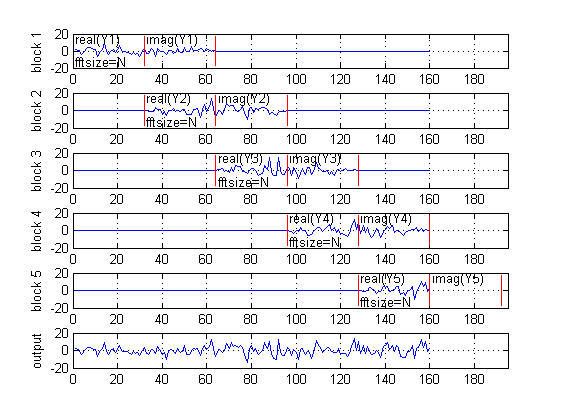
w=exp(1i*pi/2/N*(0:N-1)'); % diagonal elements for qDFT hs=fft(w.*h'); xn=reshape(x,N,[]); x1=bsxfun(@times,w,xn); % pre-multiplication by diagonal twiddle factors s1=fft(x1); % block spectrum of input signal (qDFT size = N) s2=bsxfun(@times,hs,s1); % spectral domain multiplication y1=bsxfun(@times,conj(w),ifft(s2)); % inverse skew transform, block convolution result y2=real(y1)+[zeros(N,1) imag(y1(:,1:end-1))]; % overlap-add block combination (output is read as Y=[Re(y(0))... Re(y(N-1)), Im(y(0))... Im(y(N-1))]) ypr=reshape(y2,1,[]); % block-wise graph figure(1) % title('Proposed qDFT based method'); plot_blockwise_propose(y1,N,length(x)) % plot resulting output subplot(size(y1,2)+1,1,size(y1,2)+1); plot(ypr) axis([0 round(length(x)+N*1.1) -20 20]); grid on ylabel(['output']);
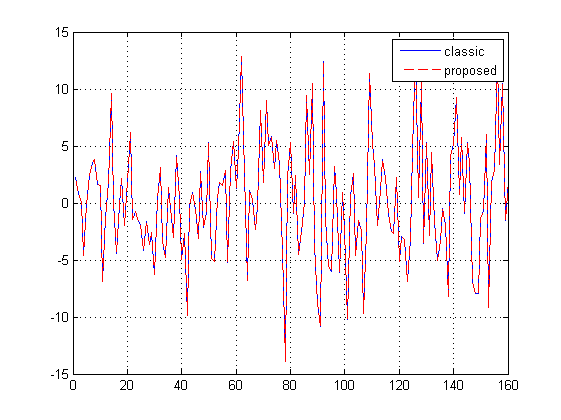
Compare results
figure(3) plot(ycl) hold on plot(ypr,'--r'); hold off grid on legend('classic','proposed')
References
[1] Blahut, R.E.: Fast Algorithms for Signal Processing. Cambridge University Press (2010). (p. 198)
[2] Jung Gap Kuk, Seyun Kim, and Nam Ik Cho, "A New Overlap Save Algorithm for Fast Block Convolution and Its Implementation Using FFT," Journal of Signal Processing Systems(Online), Feb 2010.
function []=plot_blockwise_classic(y1,N,lenx) for i=1:size(y1,2), y9=zeros(size(y1)); y9(:,i)=y1(:,i); y9=y9(1:N,:)+[zeros(N,1) y9((1:N)+N,1:end-1)]; y9=reshape(real(y9),1,[]); subplot(size(y1,2)+1,1,i); plot(y9) hold on a=17; plot([0 0]+(i-1)*N,[-a a],'r'); plot([0 0]+(i-1+2)*N,[-a a],'r'); text(1+(i-1)*N,-a*0.8,'fftsize=2N'); text(1+(i-1)*N,a*0.8,['real(Y' num2str(i) ')']); hold off axis([0 round(lenx+N*1.1) -20 20]); grid on ylabel(['block ' num2str(i)]); end function []=plot_blockwise_propose(y1,N,lenx) for i=1:size(y1,2), y9=zeros(size(y1)); y9(:,i)=y1(:,i); y9(:,2:end)=real(y9(:,2:end))+imag(y9(:,1:end-1)); y9=reshape(real(y9),1,[]); subplot(size(y1,2)+1,1,i); plot(y9) hold on a=17; plot([0 0]+(i-1)*N,[-a a],'r'); plot([0 0]+(i-1+1)*N,[-a a],'r'); plot([0 0]+(i-1+2)*N,[-a a],'r'); text(1+(i-1)*N,-a*0.8,'fftsize=N'); text(1+(i-1)*N,a*0.8,['real(Y' num2str(i) ')']); text(1+(i-1+1)*N,a*0.8,['imag(Y' num2str(i) ')']); hold off axis([0 round(lenx+N*1.1) -20 20]); grid on ylabel(['block ' num2str(i)]); end